SQL & Tableau Project: the Coronavirus Pandemic
Note: This project displays the following SQL skills:
- Filtering data
- Joins
- Grouping and Aggregation
- CTEs
- Derived tables
- Subqueries
- Views
Introduction
This analysis concerns the Coronavirus pandemic and is conducted in SQL as part of my portfolio. It is aimed at extracting and visualising data related to Covid-related deaths, vaccination rates, mortality rates and more, broken down by country, continent and time.
In this way it aims to provide important information about the success (or lack of) of different countries in combatting the pandemic. It also aims to provide a picture of how the pandemic evolved over time.
This post contains only queries and a few visualisations. The tables that the queries return, and therefore the interpretation of the tables, are not inserted or discussed. This is due to the large size of the resulting tables.
I have structured the document so that queries start simple and are country-level and progress in complexity while zooming out to global-level analysis.
A short summary of this project, including information on the data tables, columns, data types and data source can be found in a GitHub repository README file.
There is also a dashboard visualising some of the queries that are present below. But all of the visualisations in the dashboard can also be found below, attached to the relevant query.
Part 1 - Data Cleaning
Here I’m going to
- add primary keys
- change the data types of certain columns to better reflect the inherent type of data they contain
- change the date format to reflect the standard date format for SQL (yyyy-mm-dd)
- replace missing values consisting of empty strings with 0
-- add primary keys
alter table
deaths
add
id int not null auto_increment primary key first
alter tablE
vaccinations
add
id int not null auto_increment primary key first
-- format 'date' column to correct format (yyyy-mm-dd) for both tables
update
deaths
set
date = date_format(str_to_date(date,'%d/%m/%Y'),'%Y-%m-%d')
update
vaccinations
set
date = date_format(str_to_date(date,'%d/%m/%Y'),'%Y-%m-%d')
-- replace empty values in column 'total_deaths' in 'deaths' table with 0, then change data type to int
update
deaths
set
total_deaths = 0
where
total_deaths = ''
alter table
deaths
modify
total_deaths int
-- do the same as above for column 'new_deaths' in 'death' table
update
deaths
set
new_deaths = 0
where
new_deaths = ''
alter
table deaths
modify
new_deaths int
-- replace empty values for column 'continent' in 'death' table with NULL
update
deaths
set
continent = null
where
continent = ''
-- replace empty values in continent in 'new_vaccinations' table with 0
-- then change its data type to 'bigint'
update
vaccinations
set
new_vaccinations = 0
where
new_vaccinations = ''
alter
table vaccinations
modify
new_vaccinations bigint
-- replace missing values with 0 for 'people_vaccinated' and 'people_fully_vaccinated' in 'vaccinations' table
update
vaccinations
set
people_vaccinated = 0
where
people_vaccinated = ''
update
vaccinations
set
people_fully_vaccinated = 0
where
people_fully_vaccinated = ''
-- find the data which was not uploaded in 'deaths' table. This must be done because MySQL Workbench does not fully import the 'deaths' table
select
a.location
from
vaccinations a
left join
deaths b on a.id = b.id
where
b.id is null
group by
a.location
-- Data was not uploaded for every country from Urguguay (inclusive) onwards ordered
-- alphabetically, until Zimbabwe (inclusive)
Part 2 - Country-level Questions
I’m going to select a single country to narrow down the frame of the analysis. This will be Germany. Later I will expand briefly to continent-level analysis and finally global-level analysis.
Q1) How has the infection rate changed over time in Germany?
This query does not show the percentage of infected people at a given moment in time in Germany. Rather, it is a running total of all people who have been infected as a percentage of the population. This means that people who have recovered from Covid are not subtracted from the total.
SELECT
location,
date,
total_cases,
(total_cases/population)*100 as '% of Cases'
FROM
deaths
WHERE
location = 'Germany'
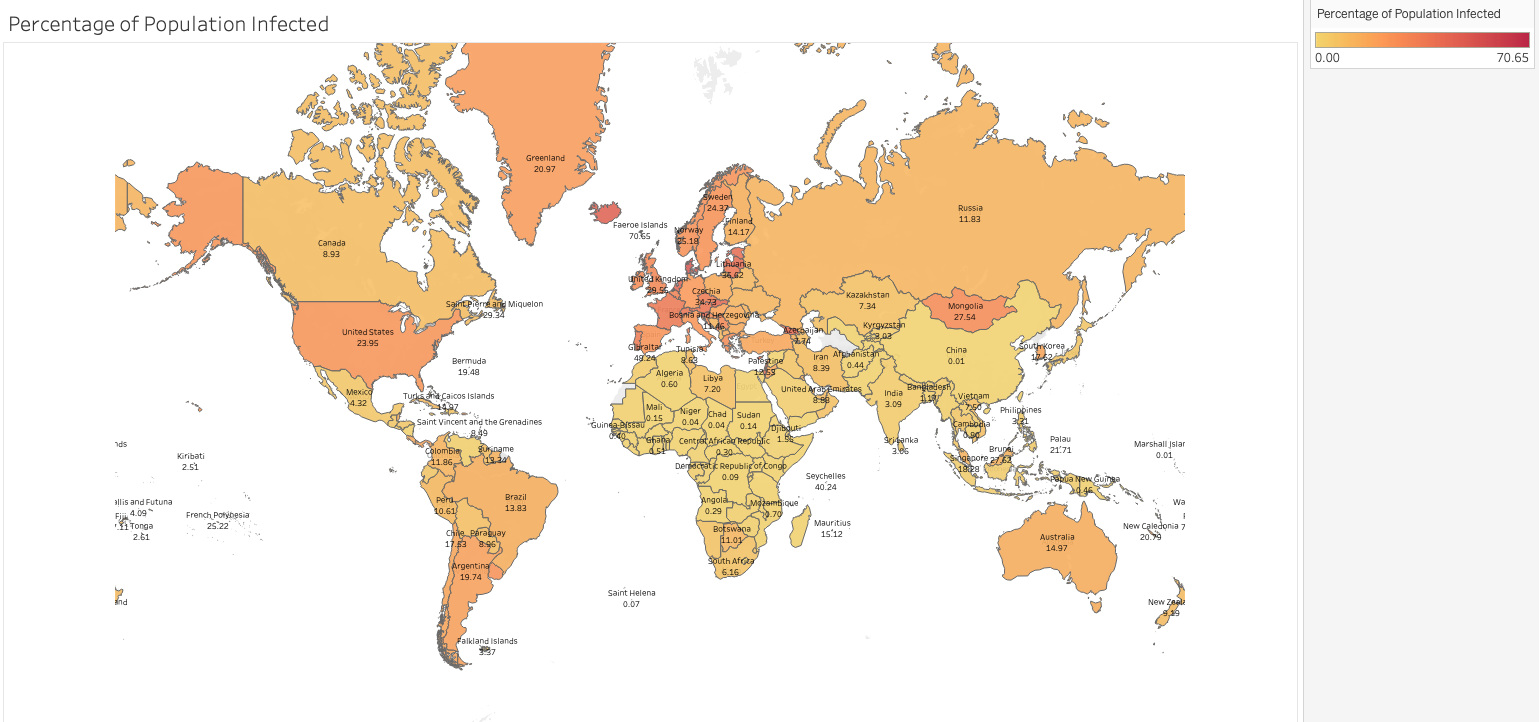
For visualisation purposes, I thought it would be more useful to show the global infection rate (that follows the above definition) as of 18/03/2022 (zoom in):
Q2) How has the mortality rate evolved over time in Germany?
select
location,
date,
total_cases,
total_deaths,
round(((total_deaths/total_cases)*100), 2) as 'Mortality Rate'
from
deaths
where
location = 'Germany'
order by
1, 2
Q3) What is the deadliest month on average in Germany?
select
location,
month(date),
round(avg((total_deaths/total_cases)*100), 2) as morality_percentage
from
deaths
where
location = 'Germany'
group by
location, month(date)
order by
morality_percentage DESC
Insight: The data suggests that the summer months have the highest mortality rate. One possible interpretation of this is that people tend to be most social and outgoing in the summer to enjoy the weather. As more people visit public places, the likelihood of the virus transmitting is greater.
But that doesn’t explain why mortality is higher. Perhaps older segments of population visit public places more and get infected, and older people are more likely to die from Covid due to weaker immune systems as a result of advanced age.
Q4) In which countries are you most likely to die from Covid today?
This data was obtained on 2022-03-18, so that is the date that will be considered ‘today’
select
location,
date,
(total_deaths/total_cases)*100 as Mortality_Rate
from
deaths
where
date = '2022-03-18'
order by
Mortality_Rate DESC
limit
5
Part 2 - Continent and Global-level analysis
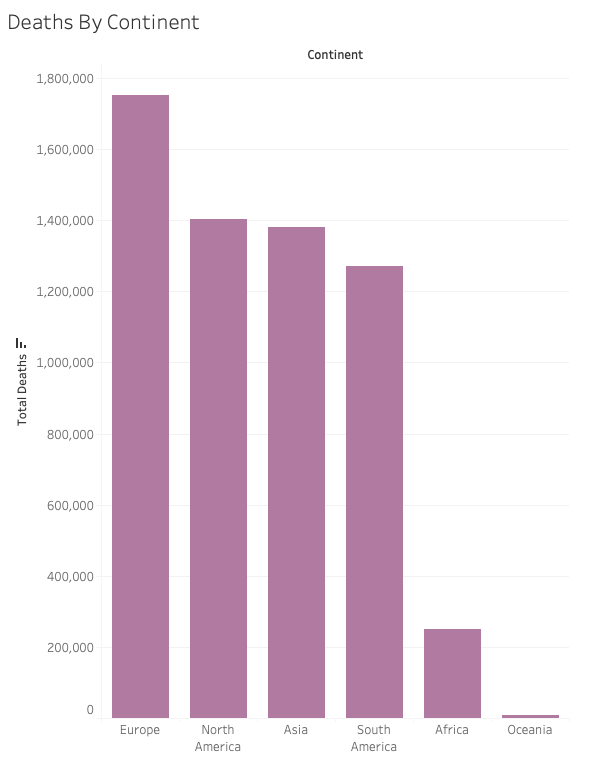
Q5) What are the global death figures by continent?
select
location, max(total_deaths) as total_continent_deaths
from
deaths
where
continent is null and
location not in('High income', 'European Union', 'Low income')
group by
location
order by
total_continent_deaths desc
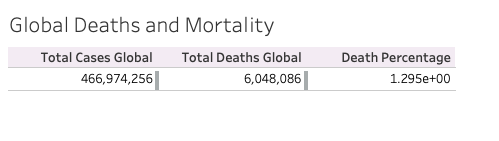
Q6) Total global cases and deaths
select
sum(new_cases) as total_cases_global,
sum(new_deaths) as total_deaths_global,
(sum(new_deaths)/sum(new_cases))*100 as death_percentage
from
deaths
where
continent is null and
location not in('European Union', 'High income', 'Low income')
Q7) How many vaccine doses have been administered as a percentage of population?
with cte1 as(
select
a.continent,
a.location,
a.date,
a.population,
b.new_vaccinations,
sum(b.new_vaccinations) OVER (Partition by a.location
order by a.location, a.date) as vacc_so_far
from
deaths a
inner join
vaccinations b using(location, date)
where
a.continent is not null)
select
location,
date,
population,
new_vaccinations,
vacc_so_far,
(vacc_so_far/population)*100 as percent_pop_vaccinated
from
cte1
Let’s create a view so we can access these results easily next time
Create view
create view global_vaccination_rate as
with cte1 as(
select
a.continent,
a.location,
a.date,
a.population,
b.new_vaccinations,
sum(b.new_vaccinations) OVER (Partition by a.location
order by a.location, a.date) as vacc_so_far
from
deaths a
inner join
vaccinations b using(location, date)
where
a.continent is not null)
select
location,
date,
population,
new_vaccinations,
vacc_so_far,
(vacc_so_far/population)*100 as percent_pop_vaccinated
from
cte1
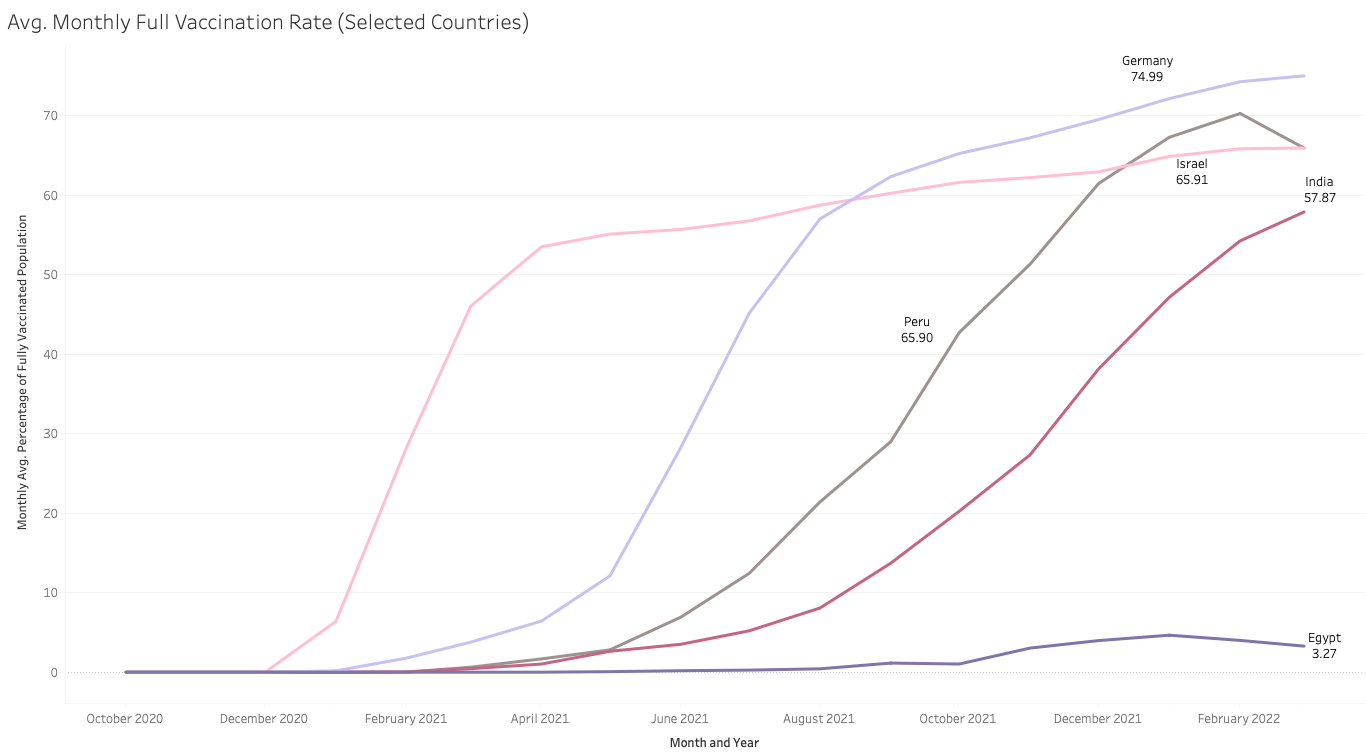
Q8) How have vaccination rates for countries changed over time?
create view global_vaccination_rates1 as
select
b.location,
a.population,
b.date,
max(b.people_vaccinated) as total_partial_vaccinations,
max(b.people_fully_vaccinated) as total_full_vaccinations,
(max(b.people_fully_vaccinated)/a.population)*100 as percentage_fully_vaccinated
from
deaths a
inner join
vaccinations b using(location, date)
group by
a.population, b.location, b.date
For visualisation purposes, I have chosen only a few countries for clarity
# Q9) Which country has had the most severe cases of covid?
select
location,
sum(total_cases) as total_cases,
max(total_cases/population)*100 as '% of Cases',
sum(icu_patients) as total_icu_patients
from
deaths
where
continent is not null
group by
location
order by
4 DESC